GRI 302: Energy 2016
EFFECTIVE DATE: 1 JULY 2018
Introduction
GRI 302: Energy 2016 contains disclosures for organizations to report information about their energy-related impacts, and how they manage these impacts.
The Standard is structured as follows:
- Section 1 contains a requirement, which provides information about how the organization manages its energy-related impacts.
- Section 2 contains five disclosures, which provide information about the organization’s energy-related impacts.
- The Glossary contains defined terms with a specific meaning when used in the GRI Standards. The terms are underlined in the text of the GRI Standards and linked to the definitions.
- The Bibliography lists references used in developing this Standard.
Background on the topic
This Standard addresses the topic of energy.
An organization can consume energy in various forms, such as fuel, electricity, heating, cooling, or steam. Energy can be self-generated or purchased from external sources, and it can come from renewable sources (such as wind, hydro, or solar) or from non-renewable sources such as coal, petroleum, or natural gas.
Using energy more efficiently and opting for renewable energy sources is essential for combating climate change and for lowering an organization’s overall environmental footprint.
Energy consumption can also occur throughout the upstream and downstream activities connected with an organization’s operations. This can include consumers’ use of products the organization sells, and the end-of-life treatment of these products.
1. Topic management disclosures
An organization reporting in accordance with the GRI Standards is required to report how it manages each of its material topics.
An organization that has determined energy to be a material topic is required to report how it manages the topic using Disclosure 3-3 in GRI 3: Material Topics 2021 (see clause 1.1 in this section).
This section is therefore designed to supplement – and not replace – Disclosure 3-3 in GRI 3.
REQUIREMENTS
- 1.1 The reporting organization shall report how it manages energy using Disclosure 3-3 in GRI 3: Material Topics 2021.
GUIDANCE
The reporting organization can also explain whether it is subject to any country, regional, or industry-level energy regulations and policies. Additionally, it can provide examples of these regulations and policies.
2. Topic disclosures
Disclosure 302-1 Energy consumption within the organization
REQUIREMENTS
The reporting organization shall report the following information:
- a. Total fuel consumption within the organization from non-renewable sources, in joules or multiples, and including fuel types used.
- b. Total fuel consumption within the organization from renewable sources, in joules or multiples, and including fuel types used.
- c. In joules, watt-hours, or multiples, the total:
- i. electricity consumption
- ii. heating consumption
- iii. cooling consumption
- iv. steam consumption
- d. In joules, watt-hours, or multiples, the total:
- i. electricity sold
- ii. heating sold
- iii. cooling sold
- iv. steam sold
- e. Total energy consumption within the organization, in joules or multiples.
- f. Standards, methodologies, assumptions, and/or calculation tools used.
- g. Source of the conversion factors used.
Compilation requirements
- 2.1 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-1, the reporting organization shall:
- 2.1.1 avoid the double-counting of fuel consumption, when reporting self-generated energy consumption. If the organization generates electricity from a non- renewable or renewable fuel source and then consumes the generated electricity, the energy consumption shall be counted once under fuel consumption;
- 2.1.2 report fuel consumption separately for non-renewable and renewable fuel sources;
- 2.1.3 only report energy consumed by entities owned or controlled by the organization;
- 2.1.4 calculate the total energy consumption within the organization in joules or multiples using the following formula:
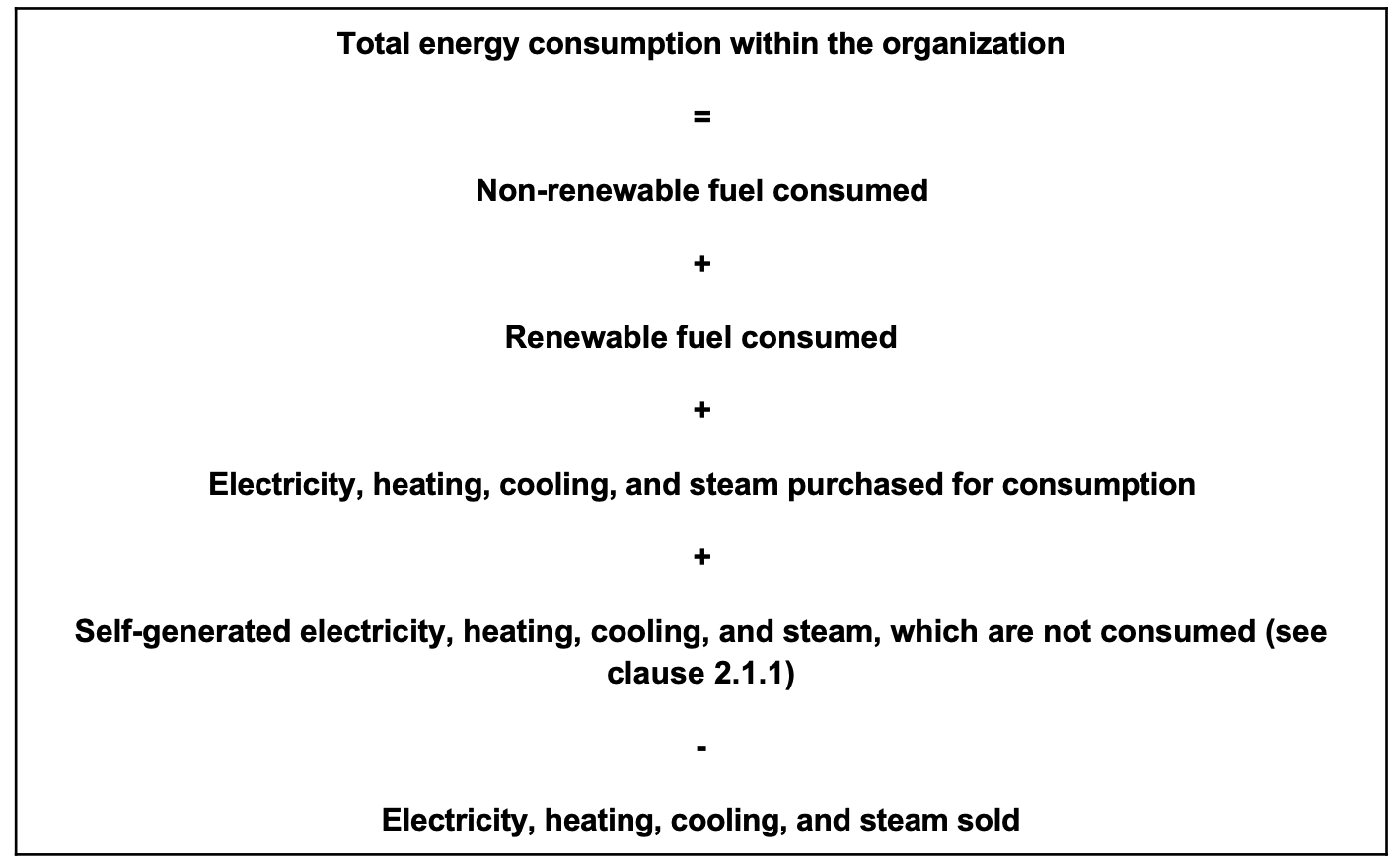
RECOMMENDATIONS
- 2.2 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-1, the reporting organization should:
- 2.2.1 apply conversion factors consistently for the data disclosed;
- 2.2.2 use local conversion factors to convert fuel to joules, or multiples, when possible;
- 2.2.3 use the generic conversion factors, when local conversion factors are unavailable;
- 2.2.4 if subject to different standards and methodologies, describe the approach to selecting them;
- 2.2.5 report energy consumption for a consistent group of entities. When possible, the group of entities should also be consistent with the group of entities used in Disclosures 305-1 and 305-2 of GRI 305: Emissions 2016;
- 2.2.6 where it aids transparency or comparability over time, provide a breakdown of energy consumption data by:
- 2.2.6.1 business unit or facility;
- 2.2.6.2 country;
- 2.2.6.3 type of source (see definitions for the listing of non-renewable sources and renewable sources);
- 2.2.6.4 type of activity.
GUIDANCE
Background
For some organizations, electricity is the only significant form of energy they consume. For others, energy sources such as steam or water provided from a district heating plant or chilled water plant can also be important.
Energy can be purchased from sources external to the organization or produced by the organization itself (self-generated).
Non-renewable fuel sources can include fuel for combustion in boilers, furnaces, heaters, turbines, flares, incinerators, generators, and vehicles that are owned or controlled by the organization. Non-renewable fuel sources cover fuels purchased by the organization. They also include fuel generated by the organization’s activities – such as mined coal, or gas from oil and gas extraction.
Renewable fuel sources can include biofuels, when purchased for direct use, and biomass in sources owned or controlled by the organization.
Consuming non-renewable fuels is usually the main contributor to direct (Scope 1) GHG emissions, which are reported in Disclosure 305-1 of GRI 305: Emissions 2016. Consuming purchased electricity, heating, cooling, and steam contributes to the organization’s energy indirect (Scope 2) GHG emissions, which are reported in Disclosure 305-2 of GRI 305: Emissions 2016.
Disclosure 302-2 Energy consumption outside of the organization
REQUIREMENTS
The reporting organization shall report the following information:
- a. Energy consumption outside of the organization, in joules or multiples.
- b. Standards, methodologies, assumptions, and/or calculation tools used.
- c. Source of the conversion factors used.
Compilation requirements
- 2.3 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-2, the reporting organization shall exclude energy consumption reported in Disclosure 302-1.
RECOMMENDATIONS
- 2.4 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-2, the reporting organization should:
- 2.4.1 if subject to different standards and methodologies, describe the approach to selecting them;
- 2.4.2 list energy consumption outside of the organization, with a breakdown by upstream and downstream categories and activities.
GUIDANCE
Guidance for Disclosure 302-2
The reporting organization can identify energy consumption outside of the organization by assessing whether an activity’s energy consumption:
- contributes significantly to the organization’s total anticipated energy consumption outside of the organization;
- offers potential for reductions the organization can undertake or influence;
- contributes to climate change-related risks, such as financial, regulatory, supply chain, product and customer, litigation, and reputational risks;
- is deemed material by stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, investors, or civil society;
- results from outsourced activities previously performed in-house, or that are typically performed in-house by other organizations in the same sector;
- has been identified as significant for the organization’s sector;
- meets any additional criteria for determining relevance, developed by the organization or by organizations in its sector.
The organization can use the following upstream and downstream categories and activities from the ‘GHG Protocol Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard’ for identifying relevant energy consumption outside of the organization (see reference [2] in the Bibliography):
Upstream categories
- Purchased goods and services
- Capital goods
- Fuel- and energy-related activities (not included in Disclosure 302-1)
- Upstream transportation and distribution
- Waste generated in operations
- Business travel
- Employee commuting
- Upstream leased assets
Other upstream
Downstream categories
- Downstream transportation and distribution
- Processing of sold products
- Use of sold products
- End-of-life treatment of sold products 5. Downstream leased assets
- Franchises
- Investments
Other downstream
For each of these categories and activities, the organization can calculate or estimate the amount of energy consumed.
The organization can report energy consumption separately for non-renewable sources and renewable sources.
Background
Energy consumption can occur outside an organization, i.e., throughout the organization’s upstream and downstream activities associated with its operations.
This can include consumers’ use of products the organization sells, and the end-of-life treatment of products.
Quantifying energy consumption outside of the organization can provide a basis for calculating some of the relevant other indirect (Scope 3) GHG emissions in Disclosure 305-3 of GRI 305: Emissions 2016.
Disclosure 302-3 Energy intensity
REQUIREMENTS
The reporting organization shall report the following information:
- a. Energy intensity ratio for the organization.
- b. Organization-specific metric (the denominator) chosen to calculate the ratio.
- c. Types of energy included in the intensity ratio; whether fuel, electricity, heating, cooling, steam, or all.
- d. Whether the ratio uses energy consumption within the organization, outside of it, or both.
Compilation requirements
- 2.5 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-3, the reporting organization shall:
- 2.5.1 calculate the ratio by dividing the absolute energy consumption (the numerator) by the organization-specific metric (the denominator);
- 2.5.2 if reporting an intensity ratio both for the energy consumed within the organization and outside of it, report these intensity ratios separately.
RECOMMENDATIONS
- 2.6 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-3, the reporting organization should, where it aids transparency or comparability over time, provide a breakdown of the energy intensity ratio by:
- 2.6.1 business unit or facility;
- 2.6.2 country;
- 2.6.3 type of source (see definitions for the listing of non-renewable sources and renewable sources);
- 2.6.4 type of activity.
GUIDANCE
Guidance for Disclosure 302-3
Intensity ratios can be provided for, among others:
- products (such as energy consumed per unit produced);
- services (such as energy consumed per function or per service);
- sales (such as energy consumed per monetary unit of sales).
Organization-specific metrics (denominators) can include:
- units of product;
- production volume (such as metric tons, liters, or MWh);
- size (such as m2 floor space);
- number of full-time employees;
- monetary units (such as revenue or sales).
Background
Energy intensity ratios define energy consumption in the context of an organization-specific metric.
These ratios express the energy required per unit of activity, output, or any other organization-specific metric. Intensity ratios are often called normalized environmental impact data.
In combination with the organization’s total energy consumption, reported in Disclosures 302-1 and 302-2, energy intensity helps to contextualize the organization’s efficiency, including in relation to other organizations.
See references [1] and [3] in the Bibliography.
Disclosure 302-4 Reduction of energy consumption
REQUIREMENTS
The reporting organization shall report the following information:
- a. Amount of reductions in energy consumption achieved as a direct result of conservation and efficiency initiatives, in joules or multiples.
- b. Types of energy included in the reductions; whether fuel, electricity, heating, cooling, steam, or all.
- c. Basis for calculating reductions in energy consumption, such as base year or baseline, including the rationale for choosing it.
- d. Standards, methodologies, assumptions, and/or calculation tools used.
Compilation requirements
- 2.7 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-4, the reporting organization shall:
- 2.7.1 exclude reductions resulting from reduced production capacity or outsourcing;
- 2.7.2 describe whether energy reduction is estimated, modeled, or sourced from direct measurements. If estimation or modeling is used, the organization shall disclose the methods used.
RECOMMENDATIONS
- 2.8 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-4, the reporting organization should, if subject to different standards and methodologies, describe the approach to selecting them.
GUIDANCE
Guidance for Disclosure 302-4
The reporting organization can prioritize disclosing reduction initiatives that were implemented in the reporting period, and that have the potential to contribute significantly to reductions. The organization can describe reduction initiatives and their targets when reporting how it manages this topic.
Reduction initiatives can include:
- process redesign;
- conversion and retrofitting of equipment;
- changes in behavior;
- operational changes.
The organization can report reductions in energy consumption by combining energy types, or separately for fuel, electricity, heating, cooling, and steam.
The organization can also provide a breakdown of reductions in energy consumption by individual initiatives or groups of initiatives.
Disclosure 302-5 Reductions in energy requirements of products and services
REQUIREMENTS
The reporting organization shall report the following information:
- a. Reductions in energy requirements of sold products and services achieved during the reporting period, in joules or multiples.
- b. Basis for calculating reductions in energy consumption, such as base year or baseline, including the rationale for choosing it.
- c. Standards, methodologies, assumptions, and/or calculation tools used.
RECOMMENDATIONS
- 2.9 When compiling the information specified in Disclosure 302-5, the reporting organization should:
- 2.9.1 if subject to different standards and methodologies, describe the approach to selecting them;
- 2.9.2 refer to industry use standards to obtain this information, where available (such as fuel consumption of cars for 100 km at 90 km/h).
GUIDANCE
Guidance for Disclosure 302-5
Use-oriented figures can include, for example, the energy requirements of a car or a computer.
Consumption patterns can include, for example, 10 percent less energy use per 100 km travelled or per time unit (hour, average working day).
Bibliography
This section lists references used in developing this Standard.
References:
- World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), ‘GHG Protocol Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard’, Revised Edition, 2004.
- World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), ‘GHG Protocol Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard’, 2011.
- World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), ‘Greenhouse Gas Protocol Accounting Notes, No. 1, Accounting and Reporting Standard Amendment’, 2012.